main content start
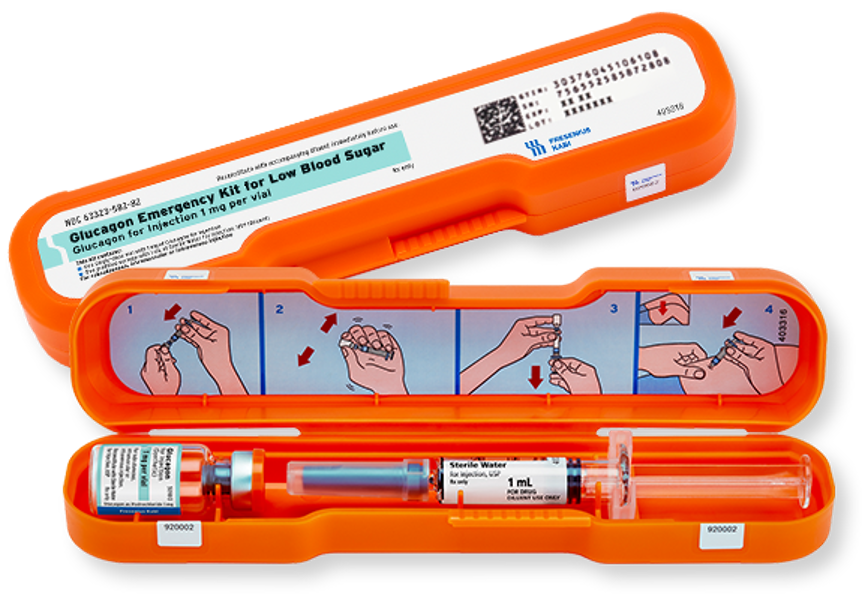
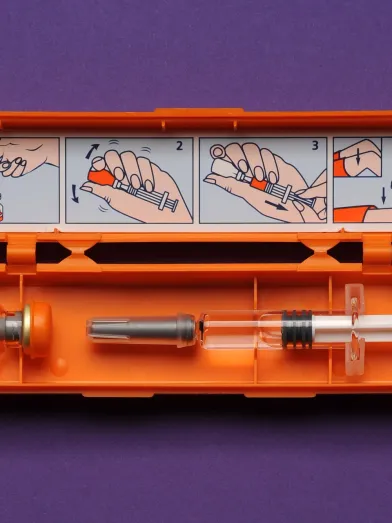
The Glucagon Emergency Kit is an injectable of glucagon used for the treatment of severe hypoglycemia in pediatric and adult patients. The kit contains a vial of glucagon and a syringe of sterile water to be mixed with the glucagon before using as an intramuscular or subcutaneous injection. Prior to reconstitution, the product can be stored for two years at room temperature. Two dosage options are available for ages 12+ as well as for 2–11 under 100 pounds.
- Emergency kit for severe hypoglycemia
- Store at room temperature
- Two-year room temp shelf life
- Comes in bright orange kit, 1 mg dosage for adults on upper arm, thigh, or buttocks
- Comes in two dosage options for ages 12+ as well as for 2–11 under 100 pounds
Glucagon Emergency Kit Specs
Key specification
Approved for Kids
12+
Shelf Life
24 month(s)
Type
Injection Requires Mixing
General Information
Product Name
Glucagon Emergency Kit
Product Type
Glucagon
Brand
Fresenius Kabi
Other Devices & Supplies
Looking for a different way to manage diabetes care? Browse and compare information on the latest devices, tools, and technology.